Responsive Design vs Adaptive Design: Which is Best for Designers?
In today’s digital era, websites must be accessible and user-friendly across a variety of devices, from smartphones and tablets to desktops and laptops. To achieve this, designers often rely on responsive or adaptive design. While both aim to enhance the user experience, they take different approaches to achieve it.
What is Responsive Design?
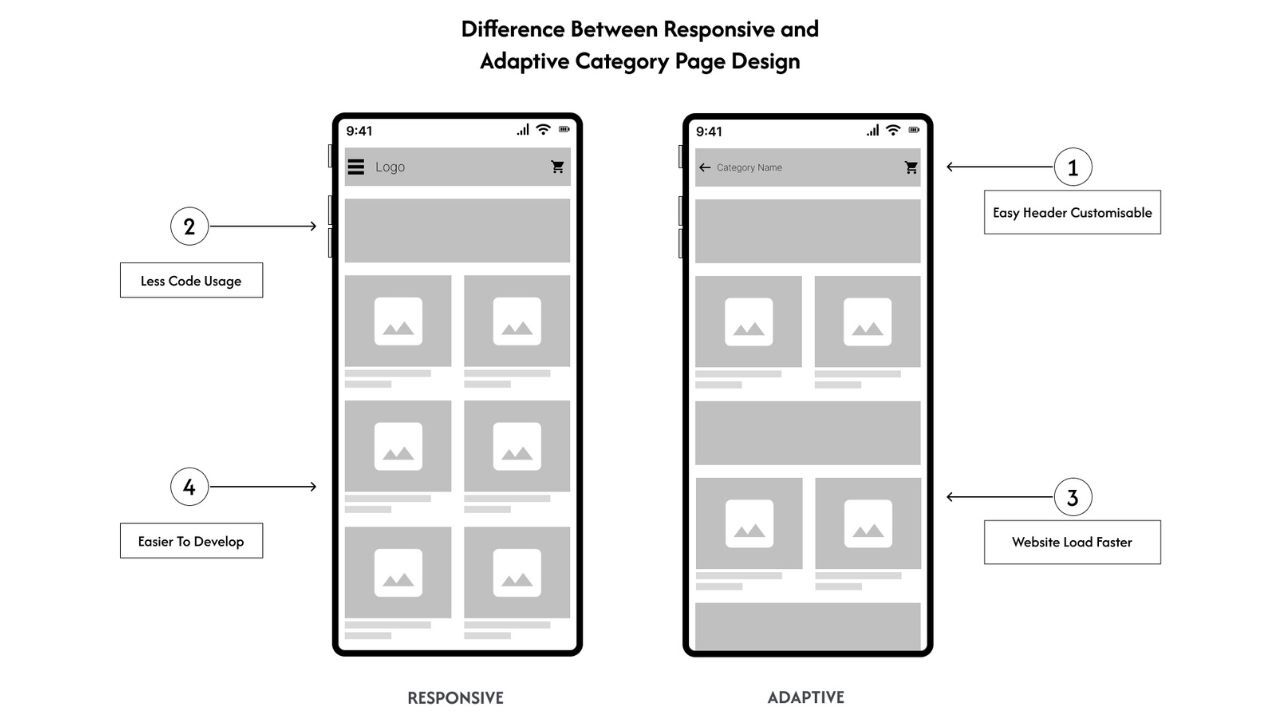
Responsive design uses fluid grids and flexible images that adjust automatically to fit the dimensions of any screen. This method typically employs a single codebase that dynamically adapts to various screen sizes, simplifying updates and maintenance.
What is Adaptive Design?
Adaptive design involves creating predefined breakpoints for specific screen sizes. Each breakpoint has its own CSS stylesheets, offering more precise control over how the website appears and functions on different devices.
Choosing the Right Design Approach
The best choice between responsive and adaptive design depends on several factors:
- Project Complexity: Responsive design works well for simpler projects with straightforward layouts.
- Control Requirements: Adaptive design is ideal for projects where precise control over the user experience is essential.
- Development Resources: Responsive design generally requires less time and fewer resources to implement and maintain.
Key Considerations
- User Experience: Ensure the design is intuitive, visually appealing, and accessible on all devices.
- Performance: Optimise for fast loading speeds, particularly on mobile devices.
- Testing: Test the site thoroughly across different devices and browsers to resolve any compatibility issues.
Advantages of Adaptive Design
- Greater Control: Offers more precise customisation for each device, ensuring an optimised experience.
- Improved Performance: Stylesheets tailored for specific screen sizes can enhance site speed.
- Enhanced User Experience: Delivers a more personalised experience by catering specifically to each device’s requirements.
When to Use Responsive Design
- Simpler Projects: Ideal for websites with straightforward layouts.
- Limited Budgets: Cost-effective and easier to develop compared to adaptive design.
- Mobile-First Approach: Perfect for projects prioritising mobile usability.
When to Use Adaptive Design
- Complex Projects: Suitable for websites with intricate layouts requiring precise customisation.
- High-Traffic Websites: Optimised performance can better handle large visitor volumes.
- Brand Consistency: Ensures uniform branding across different devices.
Conclusion
The choice between responsive and adaptive design ultimately depends on the project’s unique needs and goals. Designers should carefully assess factors such as complexity, budget, and user experience priorities to make an informed decision. By doing so, they can deliver websites that offer outstanding functionality and design across all platforms.